Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth Not all the greenhouse gas that we emit to the atmosphere remains there indefinitely For example, the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere and the amount of CO 2 dissolved in surface waters of the oceans stay in equilibrium, because the air and water mix well at the sea surface When we add more CO 2 to the atmosphere, a proportion of it dissolves into the oceans Anthropogenic greenhouse gases Drawing shows four different levels of ozone in the atmosphere At top of stratosphere, 30 miles high, ozone absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun At the top of the troposphere, 12 miles high, ozone acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heat In the middle of the tropsohere, ozone helps clean up certain pollutants

What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly
Diagram greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
Diagram greenhouse gases in the atmosphere-Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6 Once emitted into the atmosphere, they disperse widely around the globe;Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The greenhouse effect on Earth



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
By adding extra greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, people are raising the planet's temperature with wideranging impacts Carbon dioxide is neither the most potent, nor the most abundant greenhouse gas, but it is the one most responsible for altering global temperatures This close connection between climate and carbon is a compelling reason to keep track ofWater vapour is the most dominant greenhouse gas The greenhouse effect or radiative flux for water is around 75 W/m 2 while carbon dioxide contributes 32 W/m 2 ()These proportions are confirmed by measurements of infrared radiation returning to the Earth's surface (Evans & Puckrin 06)Water vapour is also the dominant positive feedback in our climate system and a majorThe presence of "greenhouse" gases in the atmosphere accounts for the temperature difference Heat radiation (infrared) emitted by the Earth is concentrated at long wavelengths and is strongly absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as water vapour, carbon dioxide and methane Absorption of heat causes the atmosphere to warm and emit its own infrared
"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Greenhouse gases greatly affect theHow the greenhouse effect works It's thought that the buildup of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways The gases allow more of the sun's rays to enter the atmosphereThe atmosphere of Earth, commonly known as air, is the layer of gases retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphereThe atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and
Figure was modified by adding the partial charges The atmosphere is, of course, actually "wet" and may contain several percent water vapor, as well as liquid and solid water in clouds, Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedThe concentration of greenhouse gases can make the atmosphere essentially opaque in a particular band If the atmosphere absorbs 100 percent of the radiation in a band the absorption will not be increased when additional greenhouse gases are added The atmosphere would then be said to be saturated in that particular frequency band However full saturation may not occur;




Greenhouse Effect Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
Carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas you hear people talk about the most That's because we produce more carbon dioxide than any other greenhouse gas, and it's responsible for most of the warming Some greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for only a short time, but others can stay in the atmosphere and affect the climate for thousands of yearsFigure b1 Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, absorb heat energy and emit it in all directions (including downwards), keeping Earth's surface and lower atmosphere warmA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3)Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download
The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere " The roots of the greenhouse effect concept lie in the 19th century, when French mathematician Joseph Fourier calculated in 14 that the Earth would be much colder if it had no atmosphere In 16, Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius was the first to link a rise in carbon dioxide gas from burning fossil fuels with a warming effect Nearly a century later, American"A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Greenhouse gases greatly affect the




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the makeup of our atmosphere Earth is sometimes called the "Goldilocks" planet – it's not too hot, not too cold, and the conditions are just right to allow life, including us, to flourishThey are removed from the atmosphereThe greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into space A simplified diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect (based on a figure in the 07 IPCC




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube
The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation) The common name given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis is air By volume, dry air contains 7809% nitrogen, 95%Main article The natural atmosphere is composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 09% argon, and only about 01% natural greenhouse gases Although a small amount, these greenhouse gases make a big difference they are the gases that allow the greenhouse effect to exist by trapping in some heat that would otherwise escape to spaceThe primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Greenhouse gases greatly affect the temperature of the Earth;




Percentage Of Greenhouse Gases In The Atmosphere Download Scientific Diagram



Annual Ghg Index Aggi
Scientists believe that the buildup of socalled greenhouse gases in the atmosphere acts like a blanket or greenhouse around the planet; Greenhouse Gases Methane, Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 3% A man scavenges for waste to recycle at a garbage dump in Linfen, China Landfill sites like this produce greenhouse gases because rotting organic waste like food waste emits methane which warms the atmosphere unless it is captured Advanced industrialsed countriesThe atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation) The common name given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis is air By volume, dry air contains 7809% nitrogen, 95%




Unit 3 Climate Change Practice Problems Flashcards Quizlet




The Greenhouse Effect Explained
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,The answer lies in the greenhouse effect — gases in our atmosphere (including CO 2, CH 4 (methane) and H 2 O water vapor) trap much of the emitted heat and then reradiate it back to Earth's surface This means that the energy leaving our planet from the top of the atmosphere is less than one would expect given the known temperature of our planet As mentioned earlier, this effectThe absorptions by CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, and O 3 are shown in the schematic diagram in the sidebar below Source The Engines of Our Ingenuity, Episode 1776, John H Lienhard, University of Houston;




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence ofThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itThe diagram outlines how the greenhouse effect works Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere The ground warms up and heat is emitted from the Earth's surface



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
The majority of the Earth's atmosphere is composed of a mixture of only a few gasesnitrogen, oxygen, and argon;Data Trends in CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O, SF 6 Obs ervation Pack age Marine Boundary Layer Reference Data Archive Products CarbonTracker CO 2 CarbonTracker CH 4 CarbonTracker Lagrange Power of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Index Information Figures Education How CO 2 is Measured Isotope Measurements WMO Standard Gas Comparisons For most of the past 800,000 years—much longer than human civilization has existed—the concentration of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere was between about 0 and 280 parts per million (In




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top
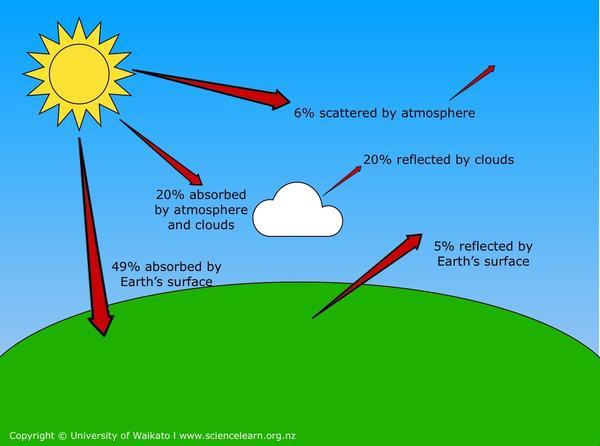



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub
Carbon dioxide, among other greenhouse gases, will remain in the atmosphere long after emissions are reduced, contributing to continuing warming In addition, as Earth has warmed, much of the excess energy has gone into heating the upper layers of the ocean Like a hot water bottle on a cold night, the heated ocean will continue warming the lower atmosphere well after greenhouse gasesThe increased amounts of greenhouse gases human activities are adding to the atmosphere have upset the balance that has been in place since the end of the last ice age Adding more greenhouse gases decreases the amount of infrared radiation energy leaving the atmosphere To get the energy back in balance, the surface of the Earth has to warm up, so that it will emit more infraredGreenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
Without them, Earth's surface would average about 33 °C colder, which is about 59 °F below the present average of 14 °C (57 °F)"Combined these three gases comprise more than 995% of all the gas molecules in the atmosphereThese gases which are most abundant within the atmosphere exhibit almost no effect on warming the earth and its atmosphere since they do not absorbA diagram of the greenhouse effect Energy flows between space, the atmosphere, and Earth's surface However, humans are adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere This is making the planet's average temperature rise by increasing the greenhouse effect The most important greenhouse gas that humans add to the atmosphere is carbon dioxide, which is now about 004% of the atmosphere



Clim2b Greenhouse Gas Effect Sources Worksheet Answers



Greenhouse Gases
As the quantities of CO 2 and the other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere rose, the temperature of the atmosphere began to increase beginning around the 1850s and has accelerated since 1950 It is this humancaused contribution of greenhouse gases and resulting global warming that is the enhanced greenhouse effect Compared to 0 years ago, the 07 levels of greenhouse gasesHeat is trapped inside the Earth's atmosphere This isThe greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary atmosphere warms the planet's surface beyond the temperature it would have in the absence of its atmosphere 39 40 41 Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's temperature would be about −18 °C (−04 °F) 42 43 compared to Earth's actual surface temperature of




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
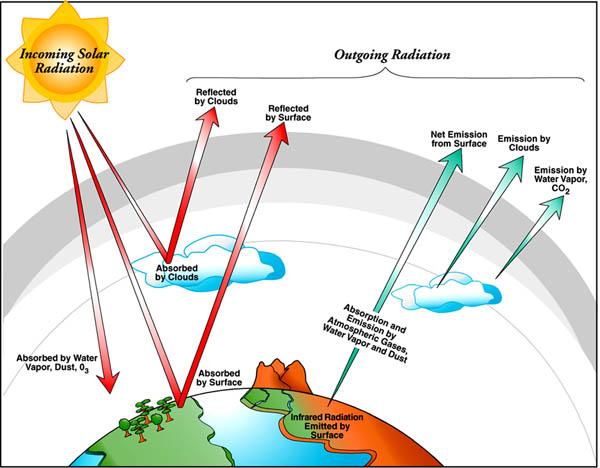



Lab 2 Climate And Earth S Energy Balance
That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere Overall, greenhouse gases are a good thing Without them, our planet would be too cold, and life as we know it would not exist But there can be too much of a good thing Scientists are worriedThe diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereAn example of greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour Infrared radiation from the Sun is only partly absorbed by the Earth The rest is radiated into the atmosphere




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences
But if the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere changes, the strength of the greenhouse effect changes too This is the cause of humanmade climate change by adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, we are trapping more heat, and the entire planet gets warmer The focus on "carbon" For climate change, the most important greenhouse gas is The carbon cycle's sinks and sources help to regulate the amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere Greenhouse Gases Besides CO 2 there are other greenhouse gases These include water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Without any greenhouse gases, Earth would be an icy wasteland Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding ontoGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases
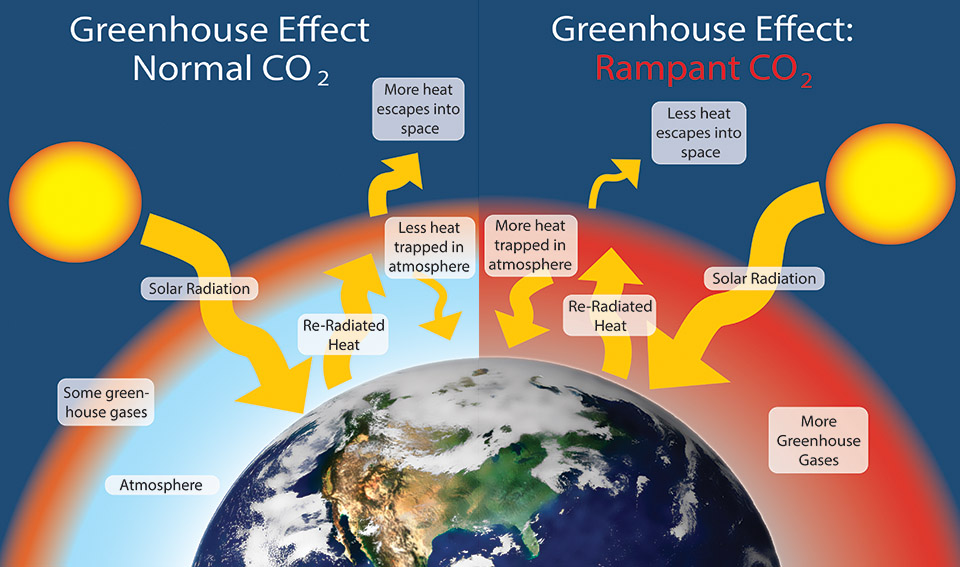



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO 2) is an acidic colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gasThe current concentration is about 004% (412 ppm) by volume, having risen from preindustrial levels of
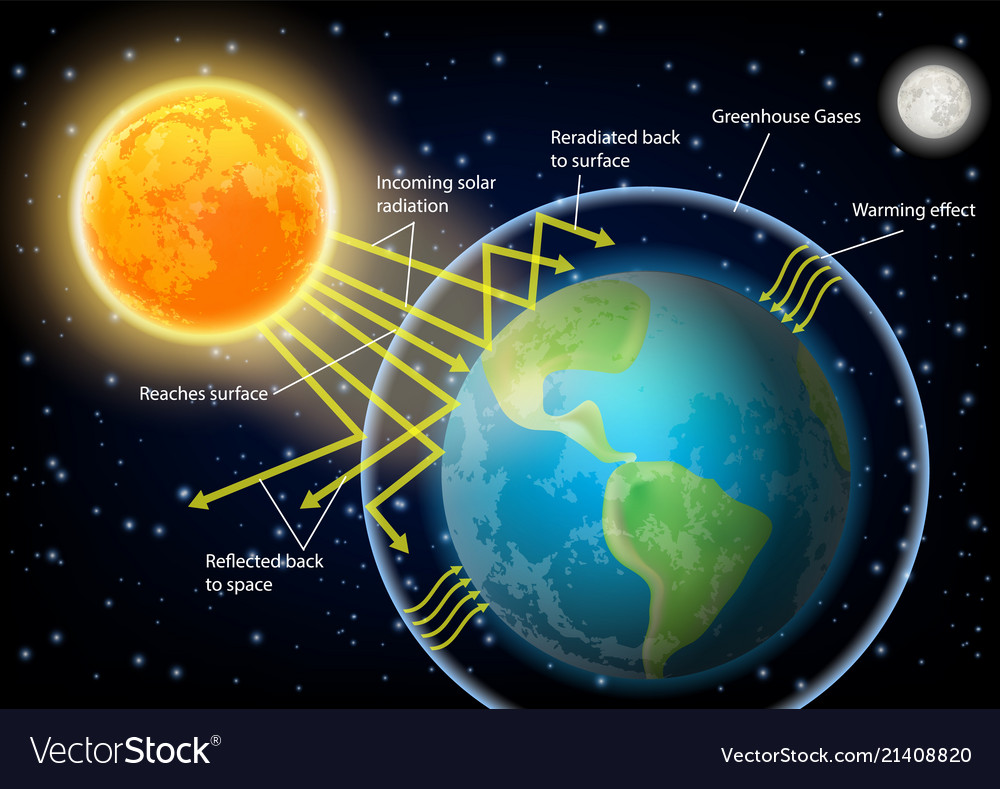



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect World101
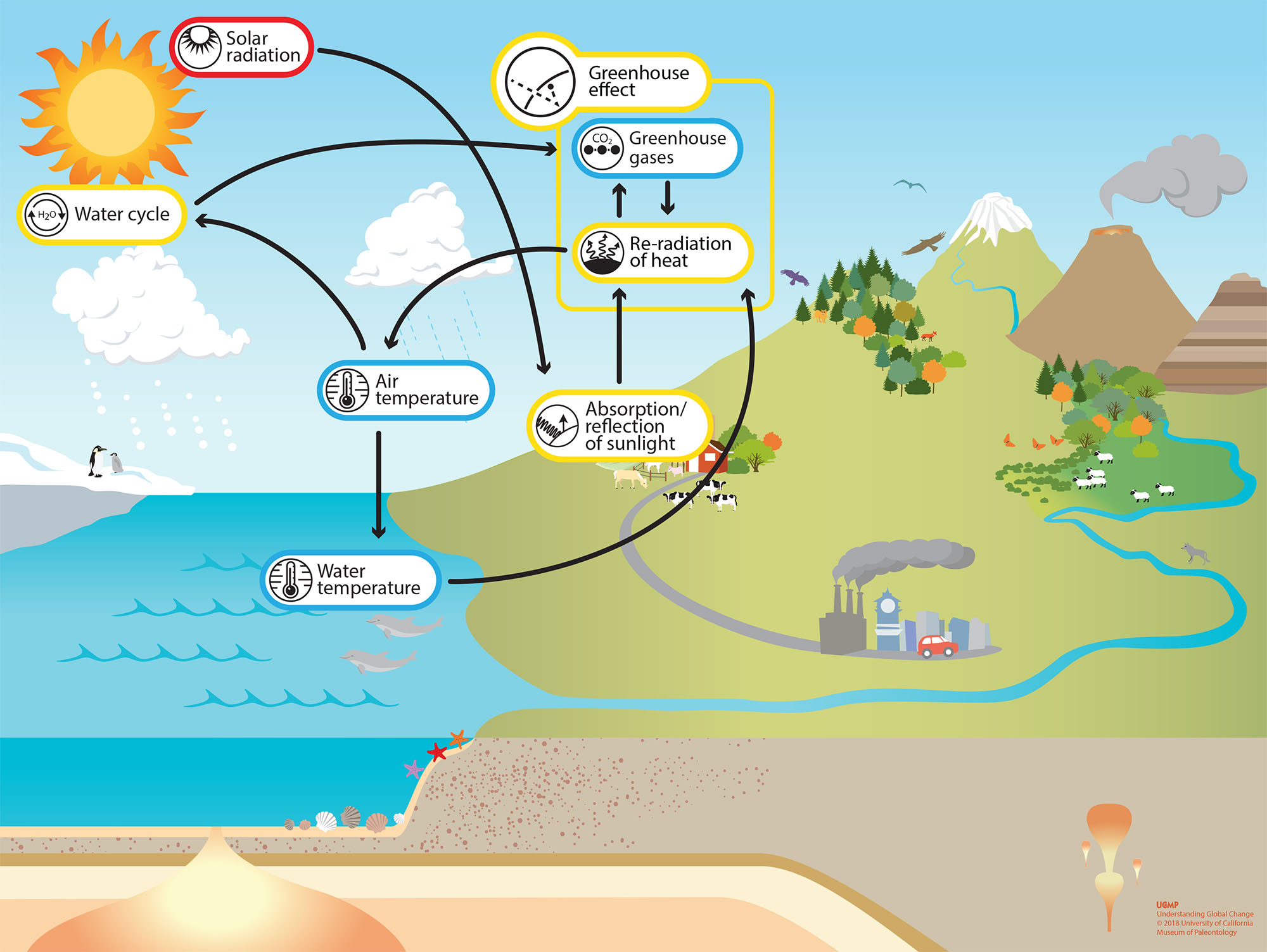



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



The Greenhouse Effect



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Experiment And Lesson For Kids




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In
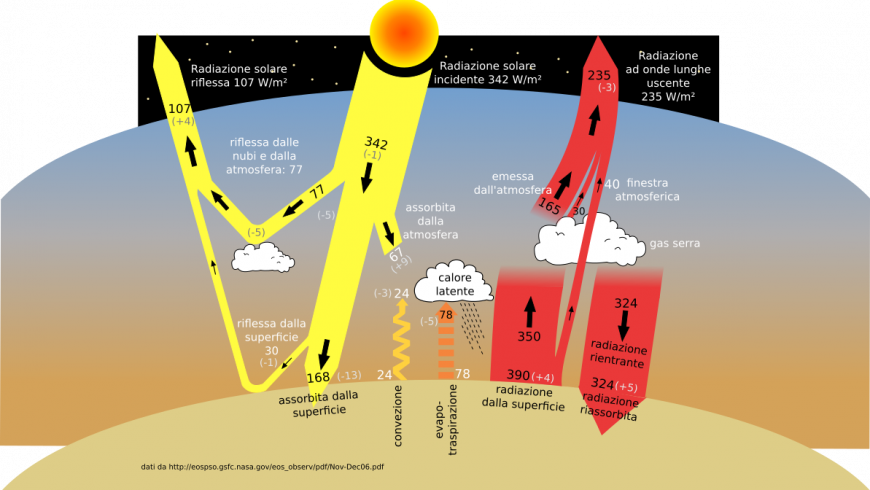



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions



The Greenhouse Effect




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education
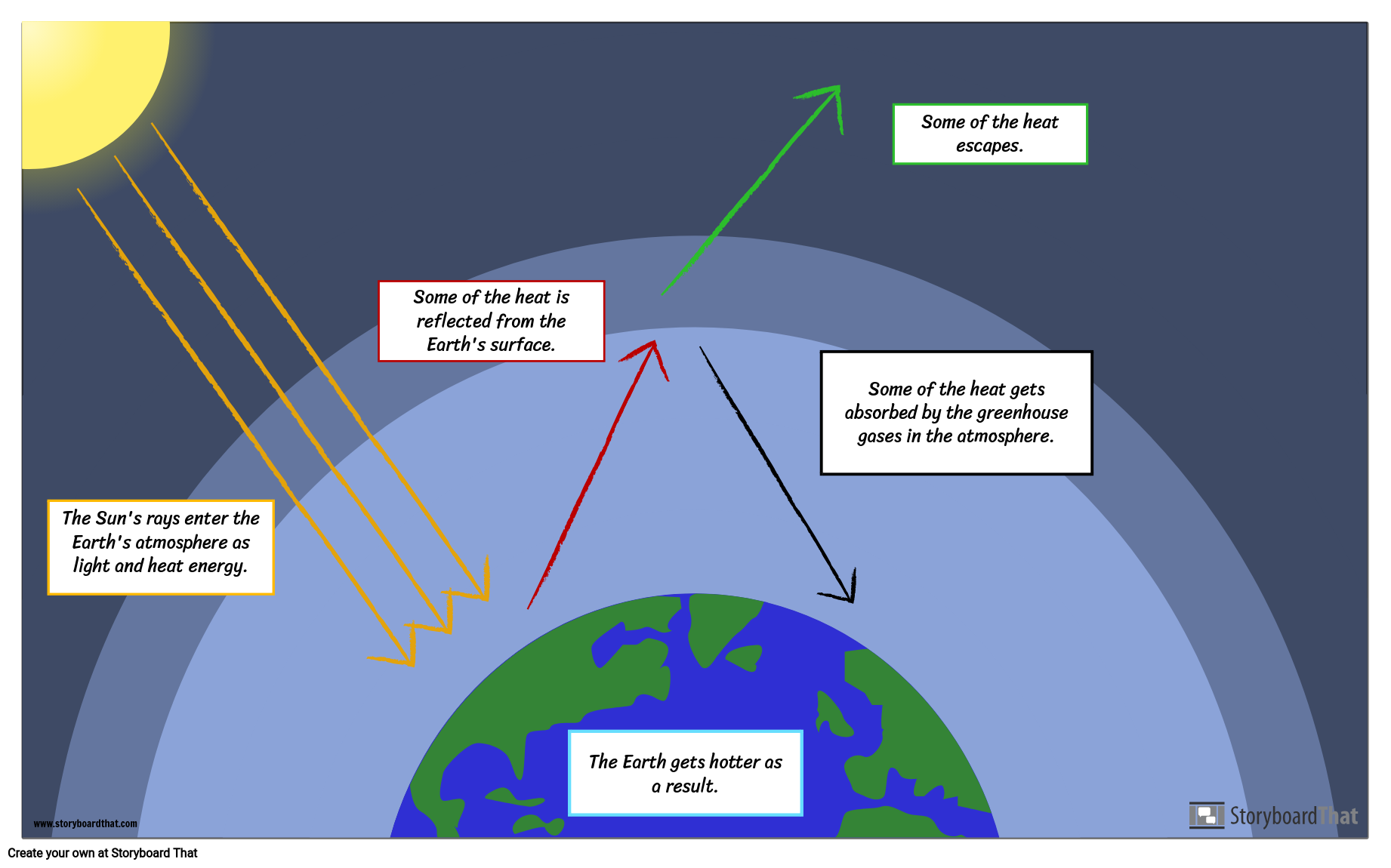



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate




Hothouse Planet S C Sea Grant Consortium



File The Green House Effect Svg Wikimedia Commons




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja




Greenhouse Effect




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons



1



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
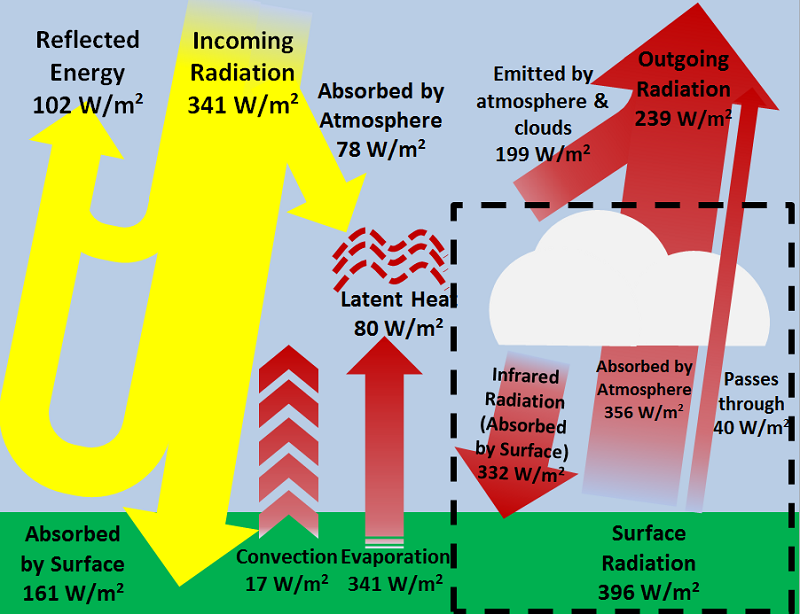



The Greenhouse Effect And Earth S Energy Budget Energy Education



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus



1




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme
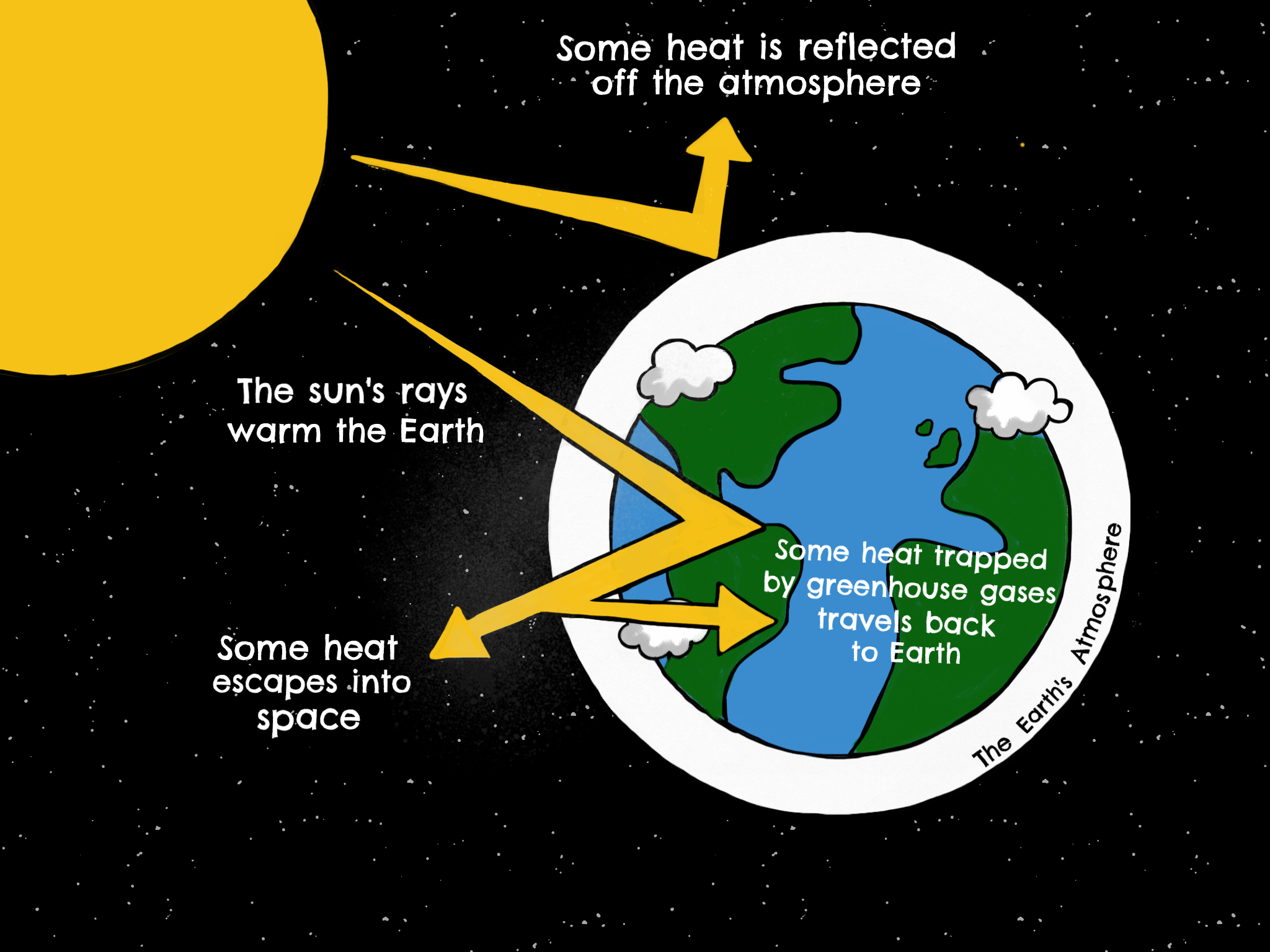



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
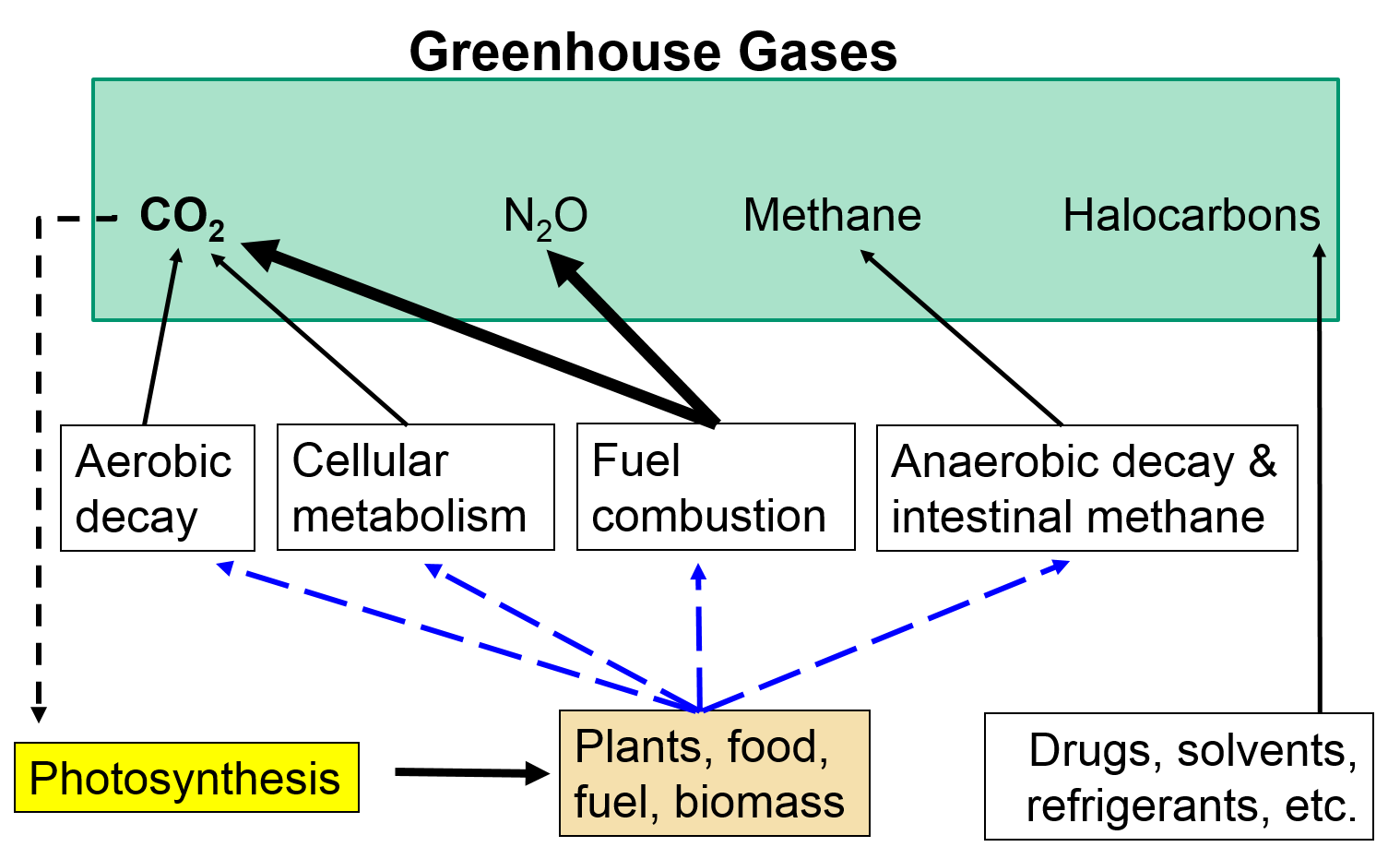



Greenhouse Gases Climate Change
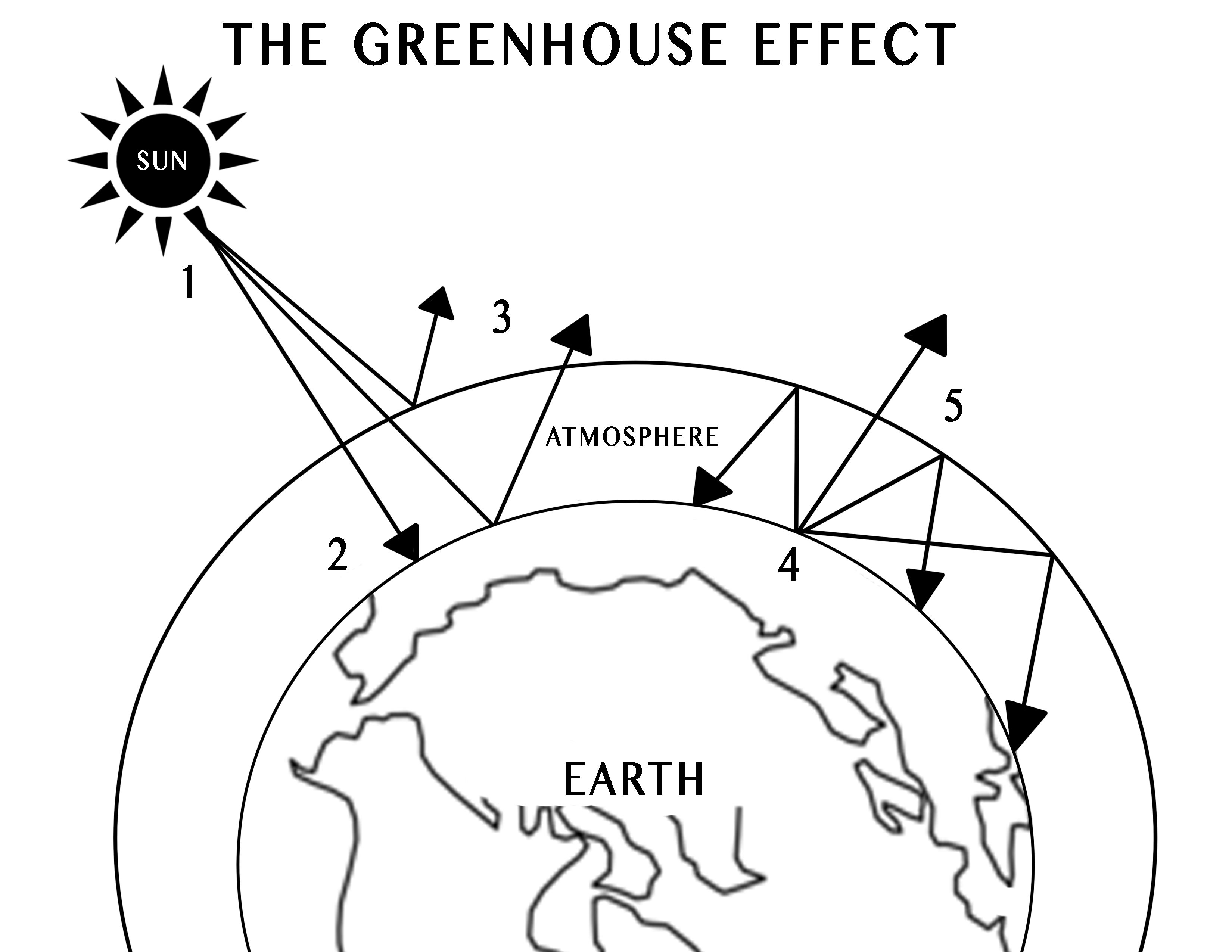



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Pie Chart That Shows Different Types Of Gases 57 Percent Is From Carbon Dioxide Fossil Fuel Use Global Warming Causes Of Global Warming Global Warming Causes




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Causes And Consequences Of A Warming Planet Agricultural Marketing Resource Center




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education
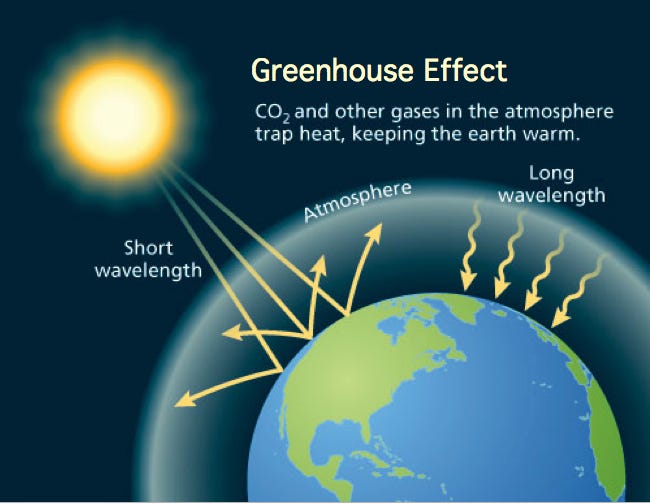



Post 5 Croatia There Is A Large Correlation Between By Monica Browne Europe At Mizzou Medium




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
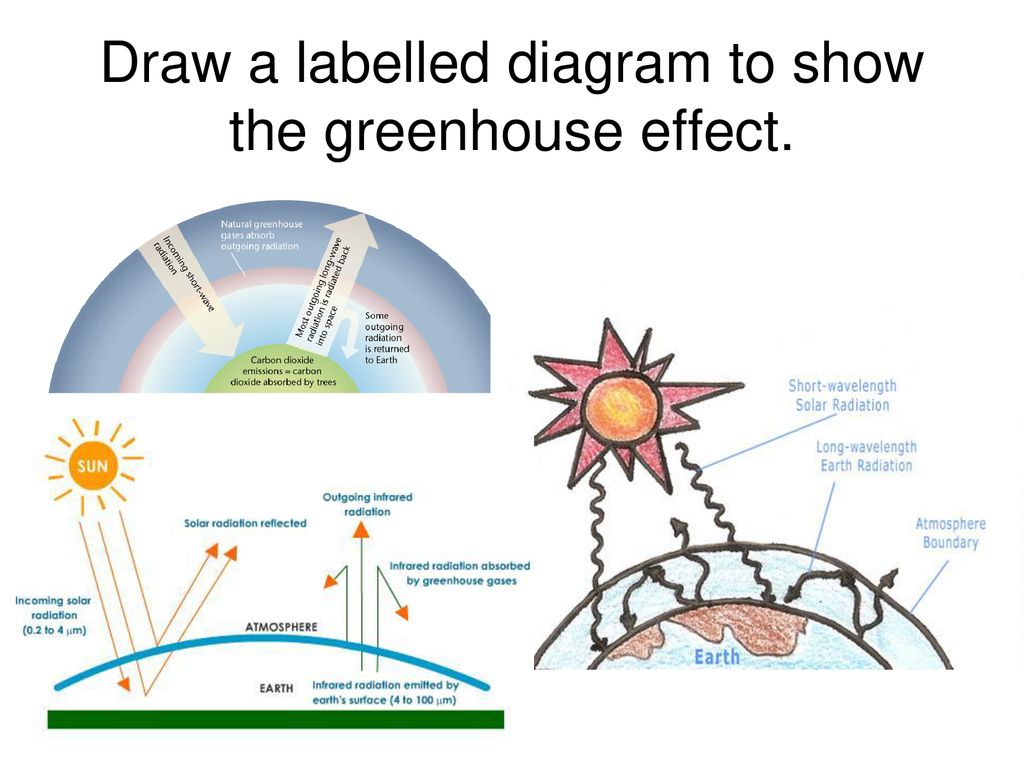



Lesson Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
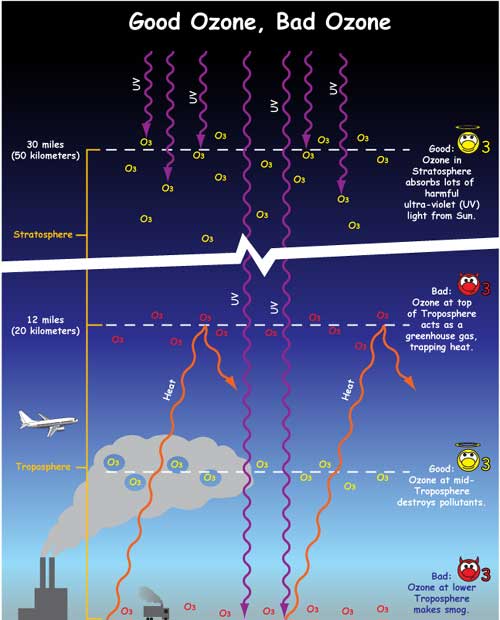



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




How Exactly Does Carbon Dioxide Cause Global Warming You Asked



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov



Untitled Document
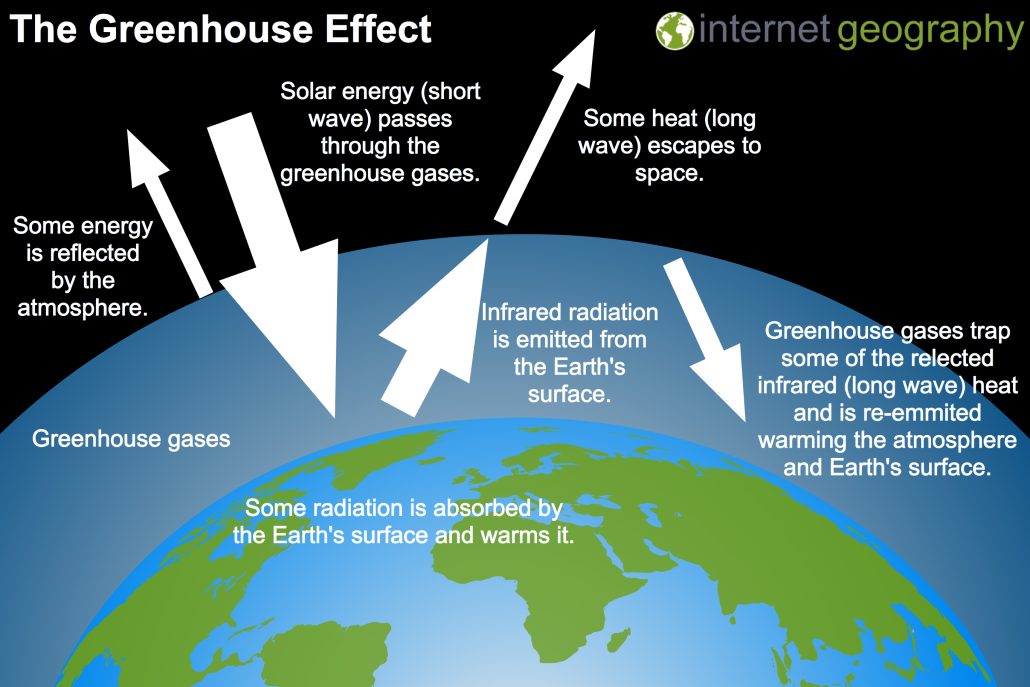



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering



1




The Greenhouse Effect World101



Www Manhassetschools Org Cms Lib8 Ny Centricity Domain 709 Greenhouse student Pdf



Untitled Document




Italki Ielts Writing Task 1 Answer 22 The Diagram Illustrates How Solar Energy Is Trapped By Greenhouse E




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Sankey Diagrams
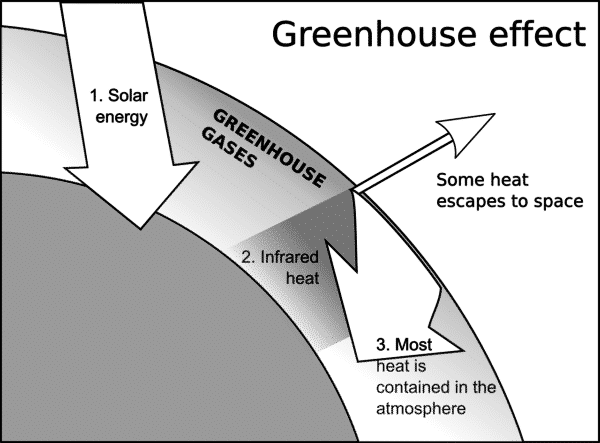



What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub




Normal Greenhouse Effect Responsible For Maintaining Constant Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Http Gzscienceclassonline Weebly Com Uploads 1 1 3 6 The Greenhouse Effect Year 9 Gz Pdf
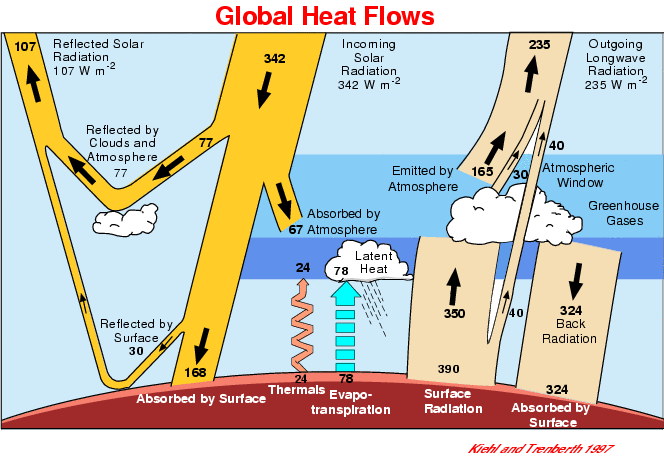



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿